课程笔记:CHI Hierarchical Instructions | Taichi
本文是 Taichi 官方教学视频的笔记:
Overview
“CHI” 含义是「气」。
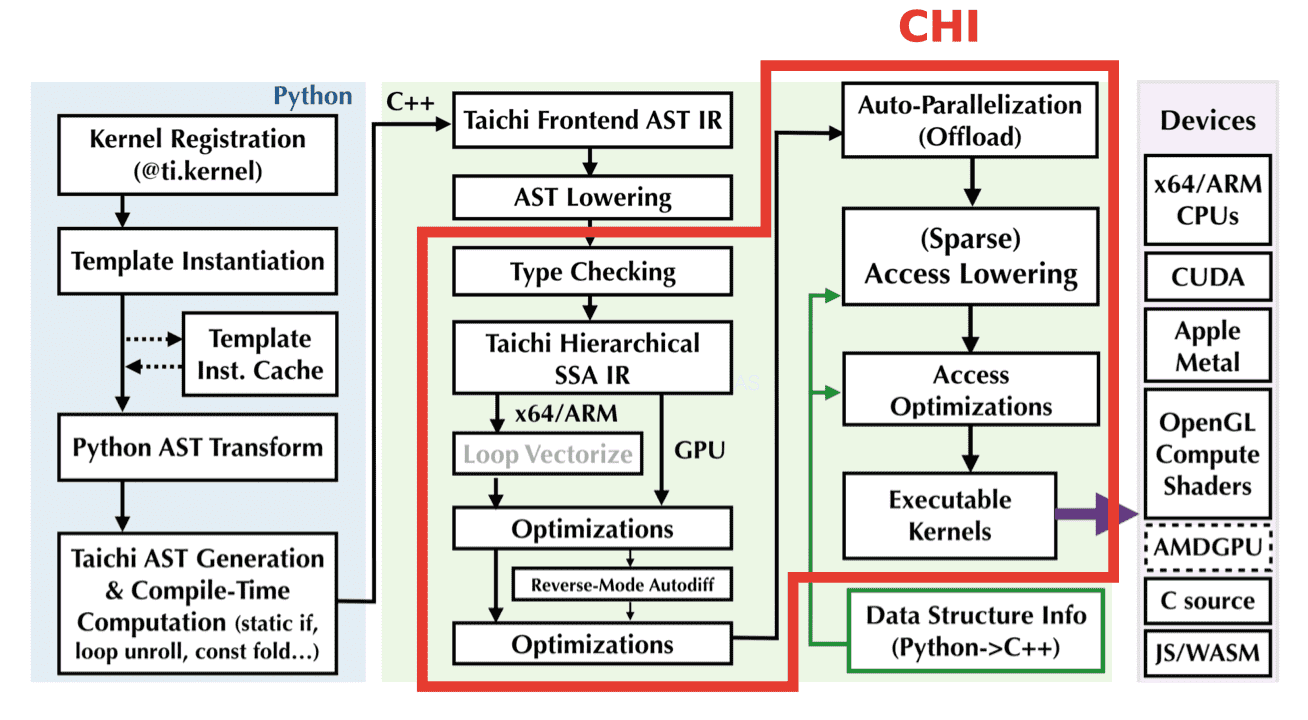
Why CHI?
- Portability
- High performance
- Taichi features
- Sparse programming
- Differentiable programming
- Quantization
- ……
Statements
- 50 statements (compared to 70 statements in Taichi codebase)
- Arithmetic: [Unary/Binary/Ternary/Atomic]OpStmt
- Memory access: [Local/Global][Load/Store/Ptr]Stmt
- Control flows: [If/RangeFor/StructFor/While/Continue/…]Stmt
- Autodiff stack operations: AdStack[Alloca/LoadTop/Pop/…]Stmt
- SNode operations: SNode[Lookup/Op]Stmt, Get[Root/Ch]Stmt
- Compiler hints: RangeAssumptionStmt, LoopUniqueStmt
- Others: PrintStmt, RandStmt, ConstStmt, AssertStmt
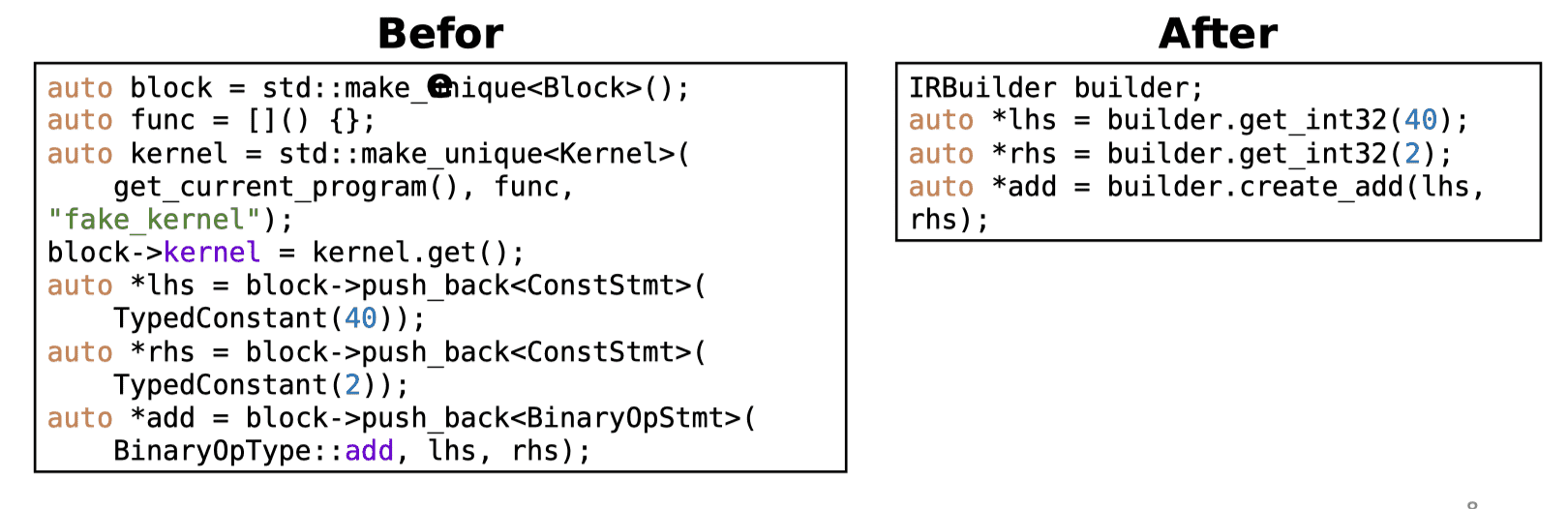
IR Builder
- An interface to generate CHI IR conveniently
- Example: generate 40 + 2:
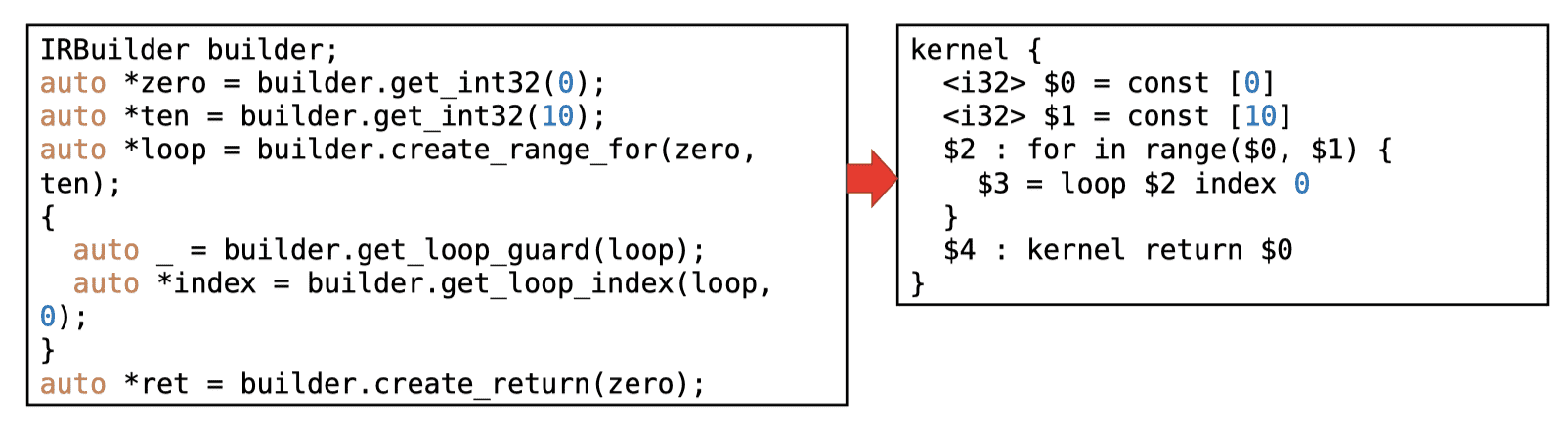
Loop guards
- Handle insertion points automatically
- WYSIWYG
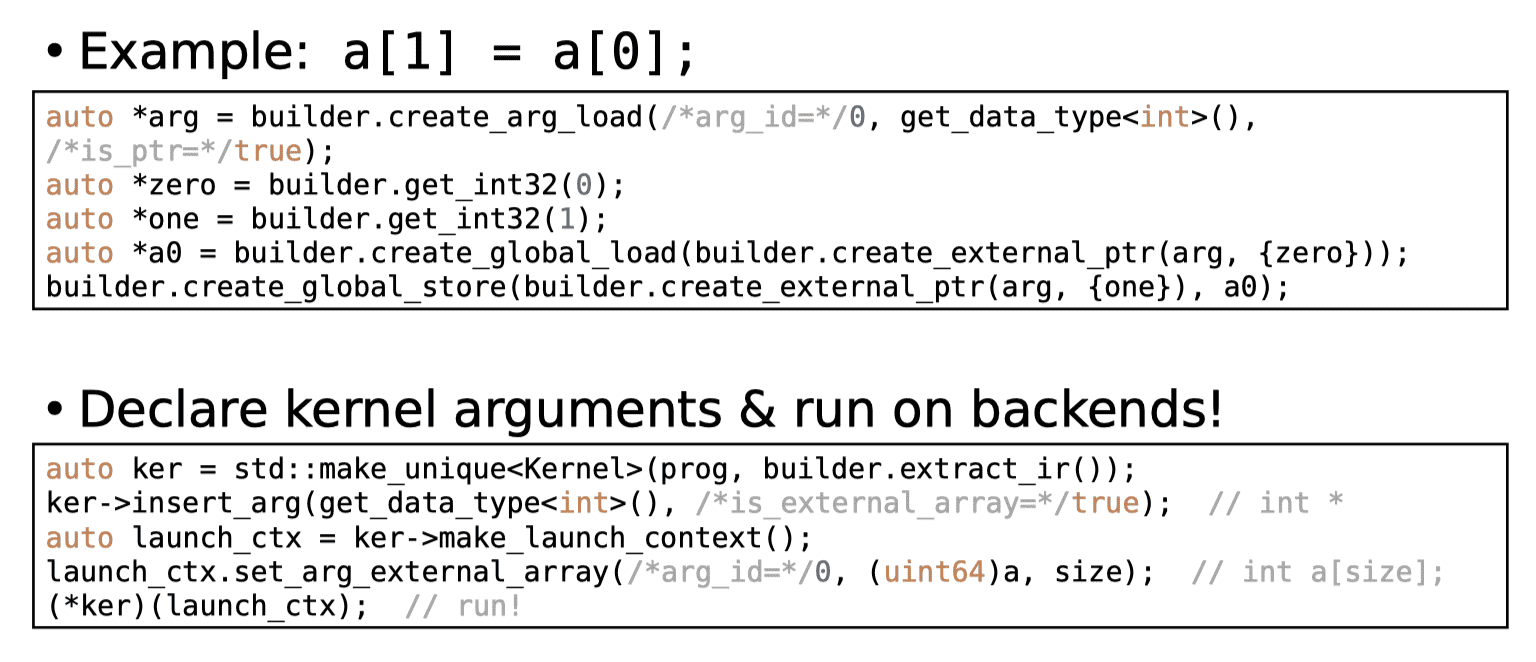
Interaction with C++ arrays
Key compilation passes
- Type checking
- (Optional) Automatic Differentiation
- Automatic Parallelization (Offload)
- Lower access
- (And many optimization passes)
Pass manager?
如果想添加自定义 compilation pass,要不要写 pass manager,直接还是用 function interface,而不是像 LLVM/TVM/SPIR-V 这种用 pass class 来 pass class。

Typical API for now:
1 | bool my_foo_pass(IRNode *ir, |
课程笔记:CHI Hierarchical Instructions | Taichi